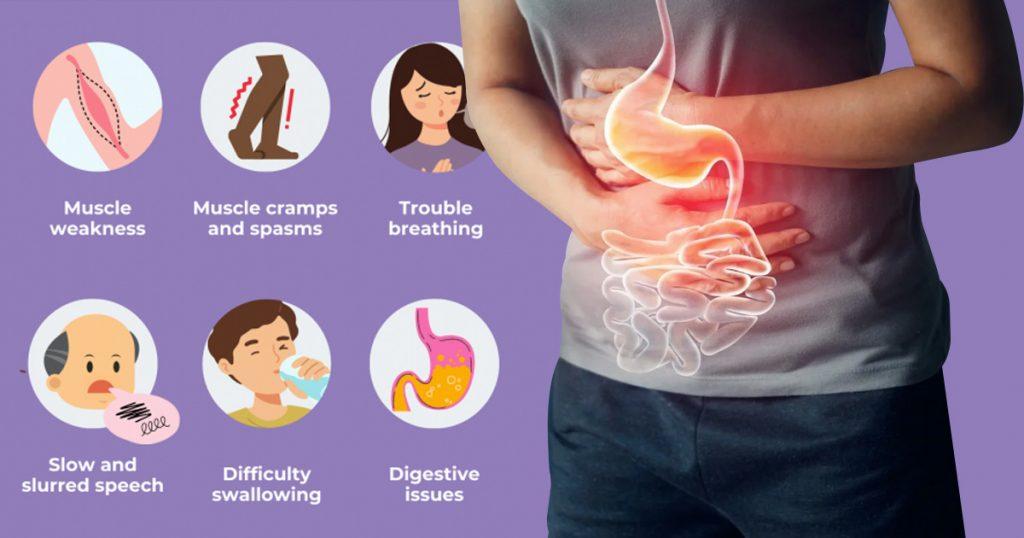
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) is a progressive neurological disease primarily known for its impact on motor neurons, leading to muscle weakness and atrophy. However, ALS can also cause significant gastrointestinal symptoms that affect the digestive system. Understanding these ALS gastrointestinal symptoms can help patients and caregivers manage the condition more effectively and maintain a better quality of life.
Causes of GI Symptoms in ALS Patients
Several factors contribute to gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms in ALS patients:
Swallowing Difficulties (Dysphagia)
Dysphagia affects up to 85% of ALS patients. This condition makes it difficult for patients to swallow food and liquids, which can lead to malnutrition and weight loss. Additionally, dysphagia increases the risk of aspiration pneumonia, where food or liquid enters the lungs.
Muscle Weakness
The weakening of abdominal and intestinal muscles in ALS patients can slow down the digestive process, leading to constipation. Constipation is a common issue, affecting up to 50% of patients. This is often exacerbated by a lack of physical activity and muscle control.
Medication Side Effects
Medications used to manage ALS symptoms can cause side effects such as ALS nausea, ALS diarrhea, and constipation. For example, riluzole, a common ALS medication, can cause gastrointestinal upset, including nausea and diarrhea.
Immobility
Reduced physical activity in ALS patients can slow gastrointestinal motility, contributing to constipation and ALS stomach pain. Immobility can also lead to muscle atrophy, further complicating digestive issues.
Nutritional Challenges
Difficulty in eating and maintaining a balanced diet can lead to gastrointestinal discomfort and symptoms such as ALS and stomach bloating. Patients may struggle to consume enough calories and nutrients, leading to further digestive complications.
Restoring Balance in ALS Patients’ Microbiomes
Maintaining a healthy microbiome is crucial for digestive health, and ALS patients can benefit from strategies to restore balance in their gut microbiome. Here are some approaches to consider:
- Probiotics and Prebiotics: Incorporating probiotics (beneficial bacteria) and prebiotics (food for these bacteria) can help support a healthy gut microbiome. Foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and fiber-rich fruits and vegetables can be beneficial. Probiotics can aid in digestion and improve overall gut health.
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated is essential to prevent constipation and support overall digestive health. ALS patients should aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day. Adequate hydration helps to keep the stool soft and easier to pass.
- Dietary Adjustments: Consuming smaller, more frequent meals can help manage ALS nausea and reduce the risk of choking. Soft, easy-to-swallow foods like smoothies, soups, and mashed vegetables can be more manageable for those with swallowing difficulties. These foods are easier to consume and digest, reducing the risk of aspiration.
- Fiber Intake: Increasing dietary fiber can help alleviate constipation. However, it’s important to introduce fiber gradually to avoid exacerbating ALS and stomach bloating or ALS stomach pain. Foods such as whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes are excellent sources of dietary fiber.
- Medications and Supplements: In some cases, doctors may recommend medications or supplements to manage specific symptoms like constipation or ALS diarrhea. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new treatment. Over-the-counter options like stool softeners or fiber supplements can be helpful.
Effects of ALS on the Digestive System
ALS has a broad impact on the digestive system, causing various symptoms and complications:
Constipation
Affects up to 50% of ALS patients due to immobility, dietary factors, and muscle weakness. Constipation can lead to discomfort, pain, and complications like hemorrhoids.
ALS Nausea
Medications and the disease itself can cause nausea, making it challenging for patients to maintain proper nutrition. ALS nausea can result in reduced food intake and further weight loss.
Stomach Pain and Bloating
ALS stomach pain and ALS and stomach bloating can result from slow gastrointestinal motility and difficulty in digesting food. Bloating can cause discomfort and interfere with daily activities.
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Symptoms like heartburn and regurgitation are reported in about 20-30% of ALS patients, complicating their digestive health. GERD can lead to chronic irritation of the esophagus and further swallowing difficulties.
Diarrhea
ALS diarrhea can occur due to medications, infections, or dietary issues, adding to the discomfort and management challenges. Diarrhea can lead to dehydration and further complicate nutritional management.
Loss of Bowel Control
Do ALS patients lose control of their bowels? In some advanced cases, muscle weakness and nerve degeneration can lead to bowel incontinence, complicating daily life for patients and caregivers. This can be a distressing symptom that requires careful management.
Managing ALS Gastrointestinal Symptoms for Better Quality of Life
Managing ALS gastrointestinal symptoms is crucial for improving the overall quality of life for patients. By understanding the causes and effects of these symptoms and implementing strategies to maintain a balanced microbiome, ALS patients can alleviate some of their digestive issues. Key approaches include:
- Dietary Adjustments: Opting for smaller, more frequent meals and incorporating soft, easy-to-digest foods can help manage symptoms like ALS nausea and difficulty swallowing.
- Hydration: Ensuring adequate fluid intake to prevent constipation and support digestive health. Staying hydrated is essential for maintaining proper digestion.
- Probiotics and Fiber: Including probiotics and gradually increasing fiber intake to promote a healthy gut microbiome. These can help in managing constipation and improving overall gut health.
Address the Issues for ALS Relief
ALS patients can better manage their digestive health by managing the symptoms, leading to improved comfort and well-being. Understanding and managing symptoms such as ALS nausea, stomach pain, bloating, and diarrhea is vital. Additionally, knowing whether ALS patients lose control of their bowels can help in preparing and managing these symptoms effectively. Improving the management of gastrointestinal symptoms in ALS not only enhances physical health but also contributes to a better quality of life for patients and their caregivers.