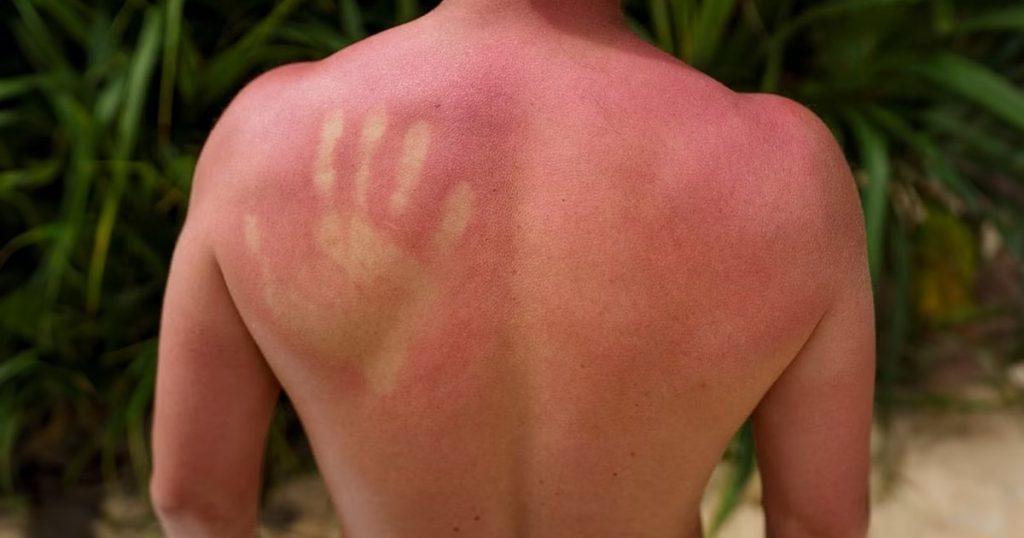
Sunburn and sun poisoning are both skin reactions resulting from excessive exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. While sunburn is more common and typically less severe, sun poisoning represents a more intense and potentially dangerous reaction. To protect your skin and health as a whole, you should know the difference between these skin conditions.
Sunburn: A Common Skin Condition
When the skin is overexposed to ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun or man-made sources like tanning beds, it burns. It has skin that is red and swollen and may feel warm or painful to the touch. Sunburn typically develops within a few hours of excessive sun exposure and can range from mild to severe, with symptoms like blistering and peeling in more severe cases.
Sun Poisoning: A Severe Reaction to Sun Exposure
Sun poisoning, on the other hand, is a more severe reaction to sun exposure that goes beyond the typical symptoms of sunburn. It can manifest in different ways, including:
- Polymorphic Light Eruption (PMLE): A condition characterized by a rash, itching, or redness, often appearing on sun-exposed areas of the body.
- Solar Urticaria: An allergic reaction to sunlight that causes hives, itching, and swelling upon exposure to UV rays.
Sun poisoning without sunburn happens when you have symptoms like nausea, fever, headache, and dehydration from too much sun, but your skin doesn’t get red or blistered like in a regular sunburn. This can occur in conditions like PMLE or solar urticaria, where your skin reacts differently to sunlight. To avoid getting it, stay out of the sun for too long, wear protective clothes, and put on sunscreen. If you have these sun sickness symptoms without sunburn, see a doctor for advice.
Difference Between Sunburn and Sun Poisoning
Sunburn and sun poisoning are both skin reactions that happen when you are in the sun for too long. They are different, though, in terms of how bad they are, what signs they have, and how they work. Here are the key differences between the two:
- Severity: Most of the time, sunburn is not as bad as sun poisoning. Sunburn usually happens on the epidermis, the top layer of skin. It can be anything from a light redness to painful burns. Sun poisoning, on the other hand, is a worse reaction that can happen deeper in the skin and may cause symptoms throughout the body.
- Symptoms: Redness, pain, and sometimes swelling or burning are signs of sunburn. As the skin heals, sunburn can also cause symptoms like itching and peeling. Sun poisoning, on the other hand, can lead to more serious symptoms like fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, headaches, and not drinking enough water. These systemic symptoms are not typically seen in sunburn alone.
- Underlying Mechanisms: UV radiation damages the DNA in skin cells, causing inflammation and the recognizable redness and pain that are symptoms of sunburn. Sun poisoning, on the other hand, may involve an allergic or immune response to UV radiation, leading to more severe skin reactions such as hives, rash, or even blistering.
- Treatment: Most sunburns and sun poisoning can be treated at home with aloe vera juice, moisturizers, cool compresses, and over-the-counter painkillers. However, severe cases of sun poisoning may require medical attention, especially if systemic symptoms are present. In this case, a doctor may suggest anti-inflammatory drugs, antihistamines, or intravenous water to help control the symptoms.
Sunburn and sun poisoning are both skin responses to UV radiation, but they are not the same in terms of how bad they are, what symptoms they show, or how they work. Understanding these differences can help you take appropriate precautions to protect your skin and health when spending time outdoors.
Sunburn vs. Sun Poisoning: When Emergency Calls
Each year, more than 33,000 sunburns necessitate emergency room visits and can affect individuals across all racial and ethnic backgrounds. Prior instances of sunburn, especially during youth, significantly increase the risk of developing skin cancer, particularly melanoma, the most fatal form of skin cancer.
It’s important to know when to seek medical help for sunburn or sun poisoning. Here are some guidelines:
- Mild Sunburn: Mild sunburn can usually be treated at home with remedies like cool baths, moisturizers, and over-the-counter pain relievers. However, if you develop blisters, severe pain, or a fever, it’s best to consult a healthcare professional.
- Severe Sunburn: If you have severe sunburn with extensive blistering, severe pain, fever, chills, nausea, or signs of dehydration (like dizziness or rapid heartbeat), seek medical attention promptly. Severe sunburn can lead to serious complications and may require medical treatment.
- Sun Poisoning: Sun poisoning, which includes symptoms like fever, chills, nausea, headache, and dehydration, requires medical attention. If you experience these symptoms without the typical signs of sunburn, consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment.
- Emergency Signs: If you experience severe symptoms like difficulty breathing, chest pain, confusion, or fainting after sun exposure, seek emergency medical help immediately. These signs could mean that you are having a serious reaction to the sun that needs medical help right away.
In general, if you’re unsure whether your sunburn or sun poisoning requires medical attention, it’s best to err on the side of caution and consult a healthcare professional. Based on your symptoms and medical background, they can tell you what the best thing to do is.
Prevention Tips
To keep from getting sunburned or sun poisoning, you need to protect your skin from too much sun. Here are some effective strategies:
- Use Sunscreen: Put on a broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least 30 SPF on your face, ears, neck, and any other skin that will be visible. Apply it again every two hours or right away after swimming, sweating, or cooling off with a towel.
- Seek Shade: Spend less time in full sunlight, especially from 10 a.m. to 4 p.m., when it’s the hottest. When you’re outside, look for places to put down umbrellas, trees, or other shade.
- Wear Protective Clothing: Wear clothes, hats, and sunglasses that block UV rays to stay safe. To protect yourself from the sun better, choose dark colors and fabrics that are tightly knitted.
- Avoid Tanning Beds: UV light from tanning beds can also burn you and raise your risk of getting skin cancer. Stay away from them at all costs.
- Stay Hydrated: To keep your skin supple and your body at the right temperature, drink a lot of water. Being dehydrated can make you more likely to get sunburns and other illnesses linked to the heat.
- Be Mindful of Medications: Some medicines can make your skin more sensitive to the sun. If you’re taking medicine, talk to your doctor or nurse to find out if you need to be extra careful in the sun.
- Monitor Your Skin: Check your skin often for changes or spots that don’t seem right. If you notice anything suspicious, such as new moles, changes in existing moles, or skin growths that bleed or itch, see a dermatologist promptly.
By following these tips and being mindful of sun safety practices, you can help protect your skin from sunburn and reduce your risk of sun poisoning and other sun-related health issues.
Understanding Better Sun Poisoning and.Sunburn
To avoid getting sunburned or sun poisoning, you must protect your skin from the sun’s UV rays. You can enjoy the outdoors safely by doing easy things like using sunscreen, looking for shade, dressing in protective gear, and drinking plenty of water. Keep in mind how sensitive your skin is to the sun, especially if you get sunburned easily or have a history of skin cancer. Taking steps to protect your skin can help you keep it healthy and lower your risk of getting sick or damaging your skin from the sun.