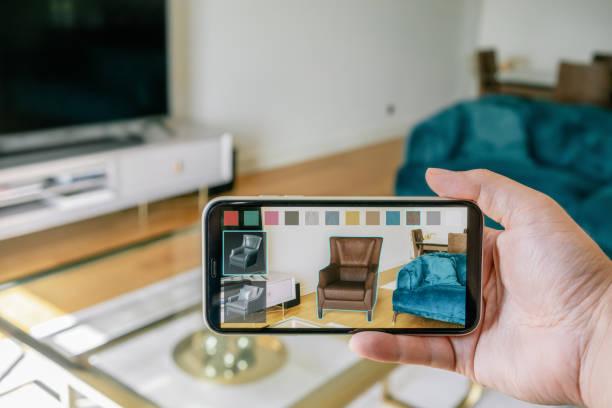
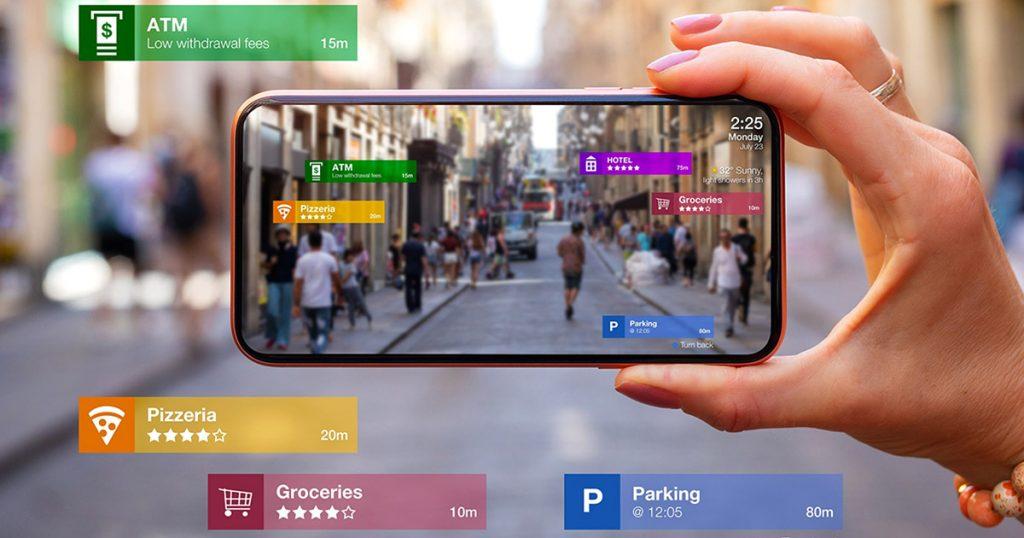
Gone are the days when augmented reality (AR) was just a figment of our imagination. The the gaming world isn’t only the one using it too. Fortunately, there are different types of augmented reality. And these allows for an engaging and interactive experience in the real world by adding virtual elements to your immediate environment.
AR works by integrating digital graphics and imagery into your visual field. These can partially or entirely substitute your un-augmented perception. Although the fundamental concept remains the same, there are several varieties of augmented reality to consider. Below are things that you should be aware of.
What is Augmented Reality?
At present, the different types of augmented reality can be produced through various applications available on conventional devices, including smartphones, tablets, Hololens, and more. As this technology continues to advance, it is seeking out new domains to enhance their workflows, particularly with the emergence of 5G technology.
In essence, augmented reality refers to a modified version of reality in which computer-generated content overlays the user’s real-life perspective, allowing digital components to be integrated into their physical surroundings.
AR must satisfy three primary characteristics:
- Fusion of real and virtual worlds.
- Interaction in real time
- Real and virtual objects are precisely registered
What are the Different Types of AR?
It is crucial to understand the various types of augmented reality (AR) and their distinctions, as each may be more appropriate for a specific application, despite sharing common traits. As a result, the primary differentiating factors include:
- Marker-based AR.
- Markerless AR:
a. Location-based AR.
b. Projection-based AR.
c. Overlay AR.
d. Contour-based AR.
Marker Based AR
AR applications that employ markers rely on target images to place objects in a designated area. These markers serve as the reference point for the application to position the 3D digital content within the user’s visual field. Markers were fundamental in early AR technologies.
To put it simply, these applications use a particular physical image pattern marker in the real-world environment to overlay a 3D virtual object on top of it. The camera constantly scans the input and identifies the marker to recognize the image pattern and generate its geometry. In situations where the camera isn’t focused correctly, the virtual object won’t appear.
Markerless Based AR
Markerless AR technology permits virtual 3D objects to be placed in the real-life image environment by analyzing real-time data features. In the world of augmented reality, the hardware in your trusty smartphone is transformed into a powerful tool for creating magical experiences. From the lens of your camera to the sensors that detect your every movement, every aspect of your device is harnessed to make the impossible possible.
Object tracking systems are no longer necessary thanks to state-of-the-art cameras, sensors, and AI algorithms that have revolutionized the way we approach augmented reality. Nowadays, augmented reality can work seamlessly without requiring any markers or trackers. Instead, it relies on advanced sensors and cameras that capture a user’s physical surroundings in real-time, transforming them into digital data that’s processed by intelligent algorithms.
Markerless analysis primarily employs simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) to scan the surroundings and create appropriate maps for virtual object placement. SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) markerless image tracking is a breakthrough technology that scans the physical environment and creates a 3D map that enables virtual objects to be accurately placed in the user’s field of view. With SLAM, users can interact with virtual objects regardless of their location or movements. This technology is particularly useful for situations where users cannot move around or scan new images.
This captivating technology has the ability to recognize objects or distinctive features in a given scene without prior knowledge of the surroundings. This technology is none other than the Markerless AR, which has the unique ability to merge computer graphics with real-world images, creating an immersive experience for users. One of the defining features of Markerless AR is its ability to detect walls, intersection points and other objects, making it ideal for creating interactive applications that respond to the user’s environment.
Location-based AR
Location-based markerless AR is a technology that blend virtual 3D objects into the physical environment where the user is located. The mechanics of this advanced AR technology revolve around the seamless integration of the virtual image with a particular location in the physical world. It’s achieved by continuously gathering and processing data from various sensors in the device. This includes the camera, GPS, compass, and accelerometer. Unlike traditional marker-based AR, this cutting-edge approach does not rely on predefined image patterns for tracking, but instead utilizes advanced algorithms to anticipate and match the user’s movements with the real-world environment in real-time.
Projection-based AR
Project-based AR is a type of augmented reality technology that aims to bring virtual 3D objects to life in a fixed physical space. By using AR, users can navigate around a defined area where a fixed projector and tracking camera are installed, enabling them to move freely in their physical space.
Overlay AR
Markerless overlay AR provides an improved version of the real world view. It’s by superimposing digital data onto the physical environment without using markers. Augmented reality technology enhances the user’s perception of an object by overlaying it with a virtual image that people can see from various angles and perspectives. It allows for a deeper understanding of the features and characteristics of the object, creating an immersive experience.
Contour-based AR
Contour-based augmented reality, also known as outlining AR. It’s a technology that utilizes simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM). It create outlines of objects and simulate realistic human interaction with them. This technique is particularly useful in low-visibility situations, such as driving at night or in heavy precipitation. An application could be developed using outlining AR to improve road safety. It’s by enhancing the visibility of objects and obstacles on the road. By using this technology, it outlines the silhouettes of objects. So making it easier for the driver to identify them and react accordingly.
Understanding the Different Types of AR for Better Use
The range of applications for the different types of augmented reality is constantly expanding and diverse. Some examples including healthcare surgical simulations, customized car design for autonomous driving promotion, and educational uses in schools. You’ll also see real-time translations, intelligent facial scanning, and military applications, among others.
However, the implementation of augmented reality is not a one-size-fits-all approach since each application has unique requirements. Marker-based AR is the most basic form of this technology, but it is not suitable for all use cases. On the other hand, markerless AR can be categorized into four distinct types. Each with unique applications and technological principles.