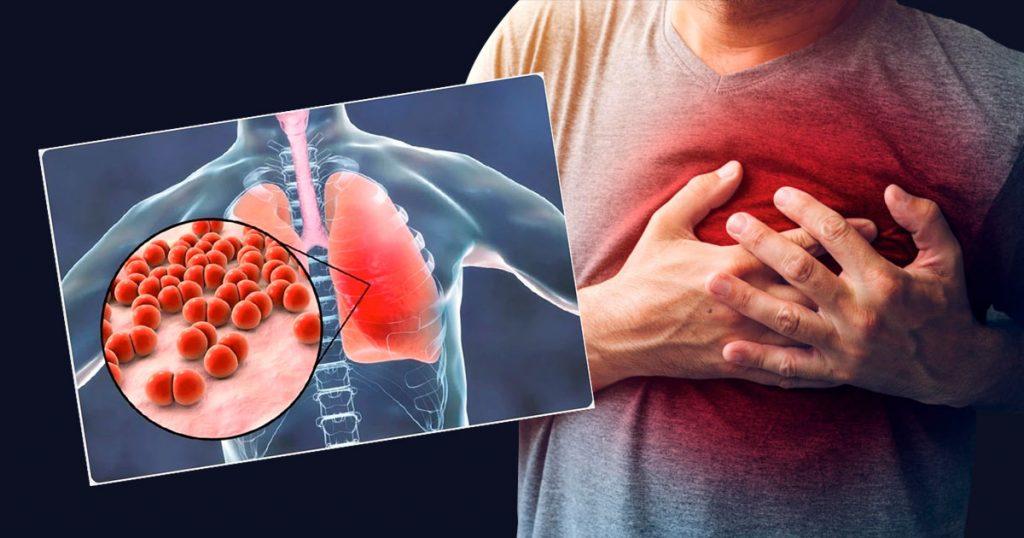
The human heart and lungs share a synergistic relationship that is crucial to our overall health. The heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body to provide nutrients and oxygen necessary for different body processes. In contrast, the job of the lungs is to draw oxygen from the air we breathe and deliver it to the bloodstream. Together, these two organs make sure the body gets the oxygen it needs.
However, problems with one or both of these organs can have a domino effect on health issues. The dual impairment of the lungs and the heart is not uncommon, as seen in conditions like heart failure and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). According to the World Health Organization (WHO), cardiovascular diseases accounted for 17.9 million deaths each year, while lower respiratory infections, including pneumonia, were responsible for over 3.2 million deaths.
Cardiac Pneumonia: A Crossroad Between Pulmonary and Cardiovascular Diseases
In the midst of the myriad conditions that can affect these organs, cardiac pneumonia stands out. But what exactly is cardiac pneumonia? Is it a lung disease or a heart disease?
Cardiac pneumonia, a term that intriguingly combines aspects of both heart and lung disease, requires our attention. This term, while not referring to a distinct illness, describes a complex situation where an individual suffering from pneumonia experiences subsequent heart complications.
Pneumonia is a lung infection that causes the air sacs in one or both lungs to become inflamed and filled with pus or fluid. This inflammation hinders the lungs’ capacity to oxygenate blood efficiently, pushing the heart to work harder to pump blood throughout the body. This increased workload on the heart can lead to additional strain on the heart muscle and, over time, potentially result in serious heart conditions like heart failure or arrhythmias.
Symptoms and Causes of Cardiac Pneumonia
Symptoms
Cardiac pneumonia typically begins with the usual symptoms of pneumonia, which can include:
- Cough that may produce phlegm
- Sweating, chills, and fever
- Breathing difficulties
- Chest pain that gets worse when you cough or breathe deeply
- Fatigue
As the heart becomes affected, additional symptoms may arise. These could include:
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Excessive sweating, especially at night
- Edema, or swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet
- More difficulty breathing, especially when lying flat
- Unexpected weight gain brought on by retention of fluid
- Decreased alertness or difficulty concentrating
These additional symptoms are indicative of the heart struggling to cope with the increased demands placed on it due to the lung infection.
Causes
The primary cause of cardiac pneumonia is a bacterial or viral pneumonia infection. When the infection leads to inflammation and fluid buildup in the lungs, the body’s oxygen supply can be compromised. In order to pump oxygen-rich blood throughout the body, the heart must then work harder, which can cause heart strain or even damage.
The chance of experiencing cardiac complications from pneumonia can be raised by specific factors. These include:
- Age: Older adults are more susceptible, as both heart function and immune system efficiency decrease with age.
- Pre-existing cardiovascular disease: Cardiac complications are more likely to occur in people who already have heart conditions.
- Chronic lung diseases: Conditions such as COPD or asthma can exacerbate the effects of pneumonia on the heart.
- Smoking: This habit can damage both the lungs and the heart, increasing vulnerability to infections and their subsequent complications.
Management and Treatment of Cardiac Pneumonia
The management and treatment of cardiac pneumonia involve addressing both the initial pneumonia infection and the associated heart complications. Here are some strategies that healthcare providers may adopt:
Treating Pneumonia
Since pneumonia is the root cause of cardiac pneumonia, it’s essential to treat the lung infection promptly. This typically involves:
- Antibiotics or Antivirals: Depending on whether the pneumonia is bacterial or viral, different medications may be prescribed to combat the infection.
- Fever reducers/Pain relievers: Over-the-counter medications might be used to manage symptoms like fever and chest pain.
- Rest and Hydration: Adequate rest helps the body recover, while staying well-hydrated aids in preventing dehydration associated with fever.
Managing Heart Complications
If pneumonia has led to heart complications, additional treatments may be necessary. These might include:
- Heart medications: These can range from drugs to control irregular heart rhythms to medications that reduce fluid buildup in the body or ones that lower blood pressure.
- Oxygen therapy: If the body isn’t receiving enough oxygen due to the lung infection, supplemental oxygen may be necessary.
- Hospitalization: In severe cases, hospital care may be required. This might involve intensive care or even the use of a ventilator in critical situations.
Prevention Strategies
Always prefer prevention to treatment. Here are a few ways to help prevent pneumonia and its potential cardiac complications:
- Vaccination: There are vaccines available that can prevent some types of pneumonia. These are especially advised for children, the elderly, those with compromised immune systems, and those suffering from long-term illnesses..
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Regular exercise, a balanced diet, adequate sleep and avoiding smoking can all contribute to better overall health, reducing the risk of lung infections and heart complications.
- Regular Check-ups: Regular medical check-ups can help detect any potential issues early and prevent them from escalating.
Prioritizing Treatment to Prevent Severe Consequences of Cardiac Pneumonia
Treating cardiac pneumonia effectively is crucial to preventing severe consequences, including heart failure or even a heart attack. The intricate link between pneumonia and cardiovascular disease underscores the importance of prompt and effective treatment.
Remember, the key to avoiding the severe consequences of cardiac pneumonia lies in early detection and prompt treatment. Regular check-ups can assist in identifying possible problems early on and halting their progression.
If you experience any symptoms of pneumonia, particularly if you have a history of lung or heart disease, it’s crucial to seek medical attention immediately. By taking these steps, you can effectively manage and treat cardiac pneumonia, reducing the risk of heart attacks and other severe complications.