ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) and CRM (Customer Relationship Management) are two systems that have changed businesses in big ways in the fast-paced world of business technologies.Businesses that want to streamline processes and improve interactions with customers need to know the difference between ERP and CRM. This article delves into the distinct functions and synergies of ERP and CRM, shedding light on how their integration can revolutionize business processes.
ERP vs. CRM: Understanding Each System
Let’s first clarify what each system means in order to gain a broad perspective on the CRM vs. ERP debate:
What is ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning)?
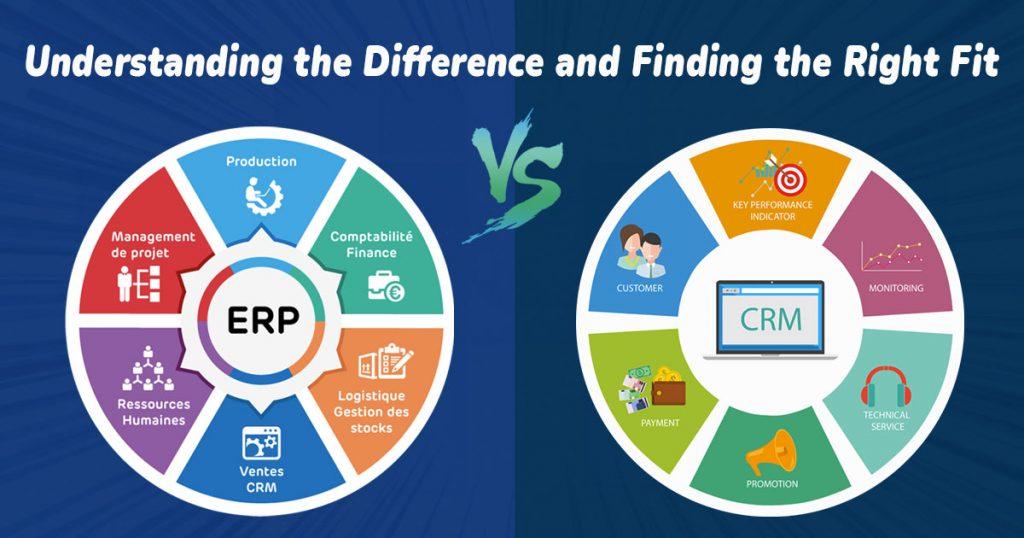
At its core, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) represents a comprehensive software solution that integrates all facets of a business operation, including inventory management, accounting, human resources, and more. The essence of ERP in CRM lies in its ability to centralize data, streamline business processes, and foster efficient decision-making. The integration of ERP systems ensures operational efficiency, a key differentiator in the ongoing CRM vs. ERP discussion.
Key Components of ERP Systems
- Supply Chain Management: ERP’s strength in optimizing the supply chain cannot be overstated. It streamlines workflow, ensuring efficient product delivery and inventory management.
- Financial Management: ERP systems are very important because they handle budgeting, accounting, and financial reports, giving you a real-time picture of how a company is doing financially.
- Human Resources Management: From recruitment to payroll, ERP encompasses all aspects of HR, thus enhancing the efficiency of human resource processes.
Benefits of Using ERP in Businesses
- Enhanced Operational Efficiency: By integrating disparate business processes, ERP systems reduce operational costs and improve efficiency.
- Improved Data Accuracy and Decision Making: Centralized data leads to more accurate analytics and informed decision-making.
- Scalability: As businesses grow, ERP systems can adapt, proving to be a flexible solution for expanding operational needs.
What is CRM (Customer Relationship Management)?
Customer Relationship Management, or CRM, is a way for a business to keep track of its interactions and relationships with present and potential customers. Unlike ERP, which focuses on streamlining internal processes, CRM is outward-facing, dedicated to enhancing customer interactions, sales growth, and service optimization. Understanding CRM vs. ERP is essential in realizing that while ERP focuses on efficiency within the company, CRM aims to improve the relationship and communication with the customer base.
Key Components of CRM Systems
- Sales Management: CRM systems help businesses understand what customers want and how they act by giving them tools to track and handle sales activities.
- Marketing Automation: Automating repetitive tasks in marketing allows for more personalized and effective customer engagement.
- Customer Support and Service: CRM helps in managing customer interactions, providing support, and enhancing overall customer satisfaction.
Benefits of Using CRM in Businesses
- Improved Customer Relationships: A CRM system provides a better understanding of customer needs and preferences, leading to stronger relationships.
- Increased Sales: By providing detailed insights into customer behavior, CRM systems can help in identifying sales opportunities.
- Enhanced Customer Service: With a better understanding of customer histories, companies can provide more effective and personalized service.
Key Differences Between ERP and CRM
The core difference in the ERP vs. CRM debate lies in their primary focus. ERP systems are made to improve and simplify business processes so that they run more smoothly and cost less. CRM, on the other hand, is all about handling relationships with customers outside of work in order to boost sales and customer service.
Focus: ERP is Internally Oriented; CRM is Customer-Oriented
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems are designed with an internal focus, aiming to integrate and automate core business processes such as finance, HR, and supply chain management. This internal orientation helps streamline operations, improve efficiency, and provide a consolidated view of organizational performance.
CRM (Customer Relationship Management) systems, on the other hand, are focused on managing interactions and relationships with customers. They put customer interaction, sales management, and marketing strategies at the top of their list of priorities, which makes customers happier and more loyal. This distinction in focus is critical in the ERP vs. CRM discussion, as it highlights the different, yet complementary, roles they play in an organization’s ecosystem.
Data Utilization: ERP Systems Streamline Operations; CRM Systems Leverage Customer Data
ERP systems excel in operational data management. They compile data from various internal sources to optimize business processes, reduce operational costs, and support data-driven decision-making. This operational efficiency is pivotal for organizational growth and stability.
On the other side, CRM systems utilize customer-related data to drive business growth. They look at interactions and comments from customers to make marketing plans better, sales processes better, and customer service better. This focus on leveraging customer data makes CRM systems indispensable for businesses looking to strengthen their market position and build long-term customer relationships.
User Base: ERP Used Across Departments; CRM by Sales, Marketing, and Service Teams
ERP systems have a diverse user base within an organization, encompassing employees from finance, operations, human resources, and more. This wide use shows how ERP helps connect different departments’ tasks into a single system. As such, ERP serves as the backbone of an organization’s internal processes.
On the other hand, the sales, marketing, and customer service teams are the ones who primarily use CRM systems. These teams rely on CRM for managing customer interactions, tracking sales leads, and developing marketing campaigns. The targeted use of CRM systems by these teams underlines their role in driving customer-focused strategies and actions, which are crucial for building and maintaining strong customer relationships.
How ERP and CRM Complement Each Other
When ERP and CRM work together, it can make a business plan that works better. ERP provides valuable data that can be used in CRM to understand customer purchasing patterns and histories. Similarly, CRM data can be used in ERP to improve inventory management based on customer demand predictions.
- Data Integration: Combining ERP and CRM allows businesses to have comprehensive insight into both internal processes and customer information.
- Streamlined Operations: With enterprise resource planning and customer relationship management integration, companies can streamline their operations and customer management, leading to increased efficiency and better customer service.
- Enhanced Analytical Data: Integrated systems provide a richer dataset for analytics, leading to more informed decision-making.
Choosing the Right System for Your Business
When considering CRM vs. ERP, businesses must assess their primary needs. If internal efficiency is the goal, ERP might be the right choice. For those focusing on customer relationships and sales, CRM should be the priority. Integration of both methods, on the other hand, is often the best way to go.
- Assess Business Needs: Understand whether the business needs improvement in internal processes, customer relationships, or both.
- Cloud-Based Solutions: For easy access and scalability, think about cloud-based ERP and CRM tools.
- Implementation Strategy: Plan for a careful and planned execution to make sure there are no problems and the change goes smoothly.
Future Trends in ERP and CRM
The ERP vs. CRM debate is always changing because of new technologies and shifting business needs. Emerging technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and the Internet of Things (IoT) are beginning to play a significant role in both ERP and CRM systems.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: These technologies are enhancing both ERP and CRM by providing deeper insights into data, predictive analytics, and automation of routine tasks.
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT integration in ERP and CRM makes it possible to collect and analyze data in real time, which helps businesses make better decisions and gives customers a better experience.
- Mobile and Cloud-Based Solutions: The shift towards mobile and cloud-based ERP and CRM solutions offers greater flexibility and accessibility, a trend likely to continue and expand.
These advancements hint at a future where enterprise resource planning and customer relationship management are not just integrated in function but also in their technological evolution, offering businesses unprecedented levels of efficiency and customer engagement.
CRM vs. ERP: Which is Better for Your Business?
People argue about whether CRM or ERP is better because they want to know what each system does well and how they can work together to make each other better. CRM is all about improving ties with customers, while ERP is all about making internal processes more efficient.
In the modern business landscape, integrating CRM with ERP is becoming not just a strategy but a necessity for businesses seeking comprehensive operational and customer management solutions. As technology continues to evolve, the synergy between ERP and CRM will only grow stronger, enabling businesses to reach new heights in operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.